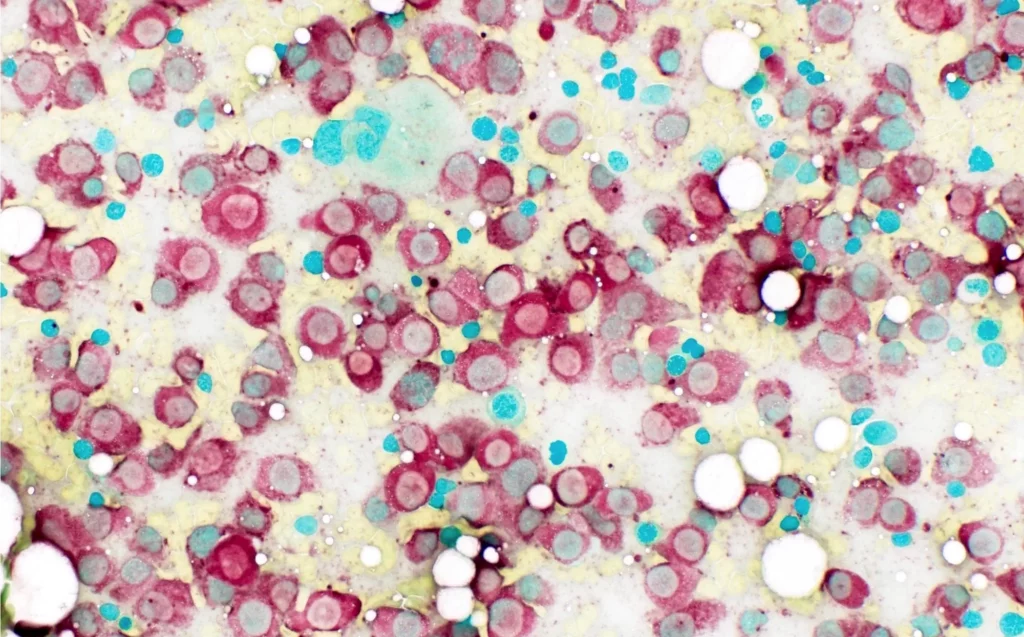
Non-Specific Esterase (NSE) Staining
Principle Leucocytes esterase are enzymes that hydrolyze acyl or chroacyl esters of alpha-napthol. There are nine isoenzymes. Five isoenzymes are stained specifically with napthol AS-D ...

Principle Leucocytes esterase are enzymes that hydrolyze acyl or chroacyl esters of alpha-napthol. There are nine isoenzymes. Five isoenzymes are stained specifically with napthol AS-D ...
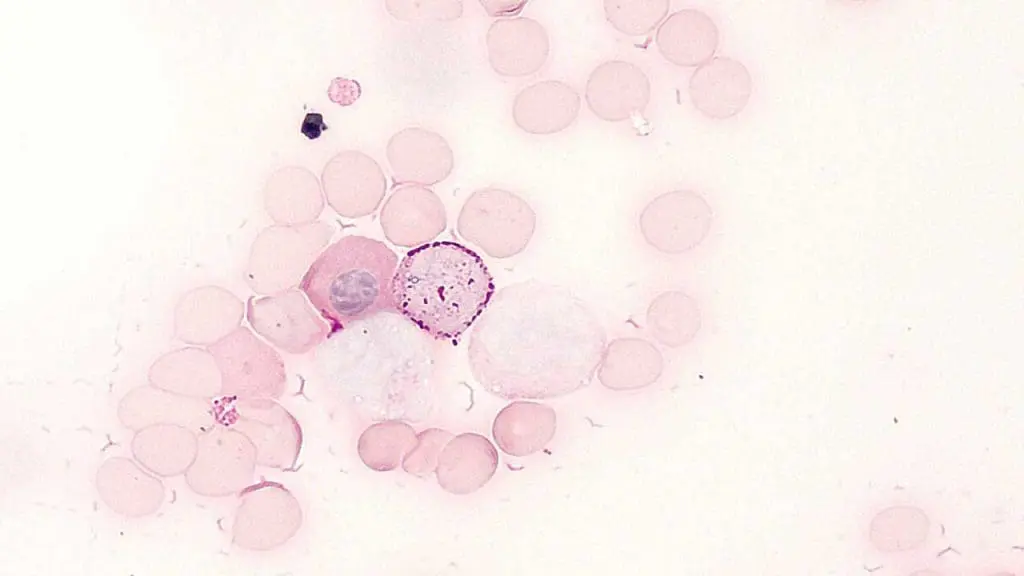
Principle: 1-2 glycol groups are oxidised by periodic acid to produce dialdehydes. The dialdehydes, when exposed to leucobasic fuchsin (Schiff’s reagent), give positive reactions in ...
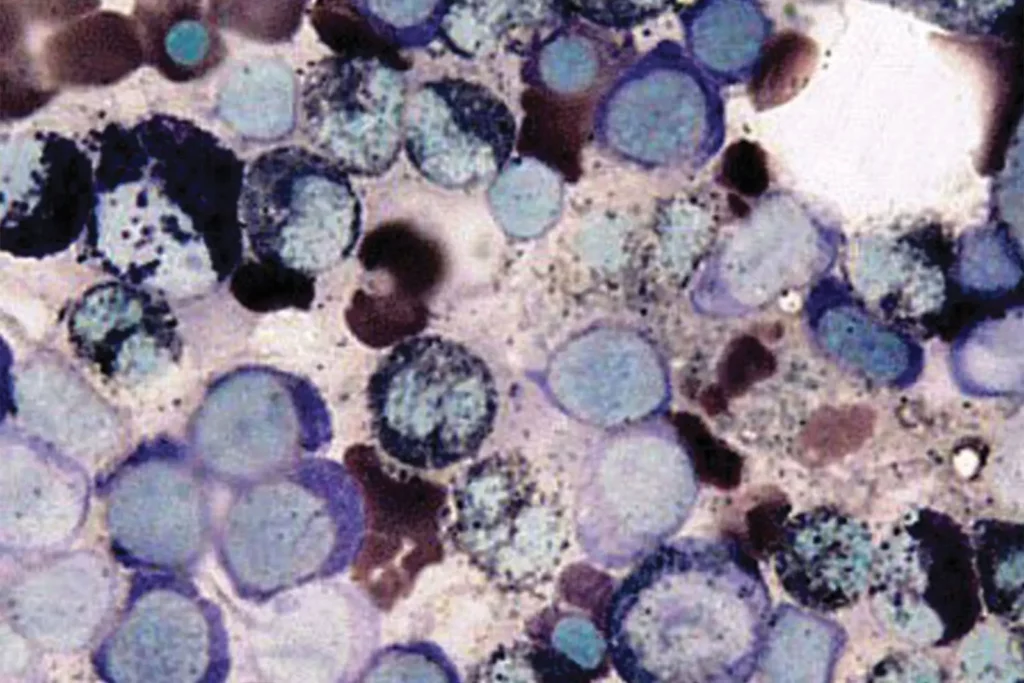
Principle Sudan black B is a lipophilic dye that binds irreversibly to an undefined granule component in granulocytes, eosinophils, and some monocytes. It cannot be ...
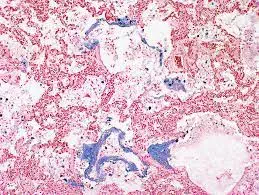
Principle The test is based on the principle of a positive Prussian blue reaction by iron particles. Non-haem iron reacts with potassium ferrocyanide to form ...
Romanowsky stains are used universally for routine staining of blood films. Principle The main components of Romanowsky stain are: 1) A cationic or basic dye ...
The film is made from a drop of blood spread evenly on a slide and stained. It is important to ensure that the film is ...